Plot posterior or prior predictive distributions. Each of these functions
makes the same plot as the corresponding ppc_ function
but without plotting any observed data y. The Plot Descriptions section
at PPC-distributions has details on the individual plots.
Usage
ppd_data(ypred, group = NULL)
ppd_dens_overlay(
ypred,
...,
size = 0.25,
alpha = 0.7,
trim = FALSE,
bw = "nrd0",
adjust = 1,
kernel = "gaussian",
bounds = NULL,
n_dens = 1024
)
ppd_ecdf_overlay(
ypred,
...,
discrete = FALSE,
pad = TRUE,
size = 0.25,
alpha = 0.7
)
ppd_dens(ypred, ..., trim = FALSE, size = 0.5, alpha = 1, bounds = NULL)
ppd_hist(ypred, ..., binwidth = NULL, bins = NULL, breaks = NULL, freq = TRUE)
ppd_dots(ypred, ..., binwidth = NA, quantiles = NA, freq = TRUE)
ppd_freqpoly(
ypred,
...,
binwidth = NULL,
bins = NULL,
freq = TRUE,
size = 0.5,
alpha = 1
)
ppd_freqpoly_grouped(
ypred,
group,
...,
binwidth = NULL,
bins = NULL,
freq = TRUE,
size = 0.5,
alpha = 1
)
ppd_boxplot(ypred, ..., notch = TRUE, size = 0.5, alpha = 1)Arguments
- ypred
An
SbyNmatrix of draws from the posterior (or prior) predictive distribution. The number of rows,S, is the size of the posterior (or prior) sample used to generateypred. The number of columns,N, is the number of predicted observations.- group
A grouping variable of the same length as
y. Will be coerced to factor if not already a factor. Each value ingroupis interpreted as the group level pertaining to the corresponding observation.- ...
For dot plots, optional additional arguments to pass to
ggdist::stat_dots().- size, alpha
Passed to the appropriate geom to control the appearance of the predictive distributions.
- trim
A logical scalar passed to
ggplot2::geom_density().- bw, adjust, kernel, n_dens, bounds
Optional arguments passed to
stats::density()(andboundstoggplot2::stat_density()) to override default kernel density estimation parameters or truncate the density support.n_densdefaults to1024.- discrete
For
ppc_ecdf_overlay(), should the data be treated as discrete? The default isFALSE, in which casegeom="line"is passed toggplot2::stat_ecdf(). Ifdiscreteis set toTRUEthengeom="step"is used.- pad
A logical scalar passed to
ggplot2::stat_ecdf().- binwidth
Passed to
ggplot2::geom_histogram()to override the default binwidth.- bins
Passed to
ggplot2::geom_histogram()to override the default binwidth.- breaks
Passed to
ggplot2::geom_histogram()as an alternative tobinwidth.- freq
For histograms,
freq=TRUE(the default) puts count on the y-axis. Settingfreq=FALSEputs density on the y-axis. (For many plots the y-axis text is off by default. To view the count or density labels on the y-axis see theyaxis_text()convenience function.)- quantiles
For dot plots, an optional integer passed to
ggdist::stat_dots()specifying the number of quantiles to use for a quantile dot plot. IfquantilesisNA(the default) then all data points are plotted.- notch
For the box plot, a logical scalar passed to
ggplot2::geom_boxplot(). Note: unlikegeom_boxplot(), the default isnotch=TRUE.
Value
The plotting functions return a ggplot object that can be further
customized using the ggplot2 package. The functions with suffix
_data() return the data that would have been drawn by the plotting
function.
Details
For Binomial data, the plots may be more useful if the input contains the "success" proportions (not discrete "success" or "failure" counts).
See also
Other PPDs:
PPD-intervals,
PPD-overview,
PPD-test-statistics
Examples
# difference between ppd_dens_overlay() and ppc_dens_overlay()
color_scheme_set("brightblue")
preds <- example_yrep_draws()
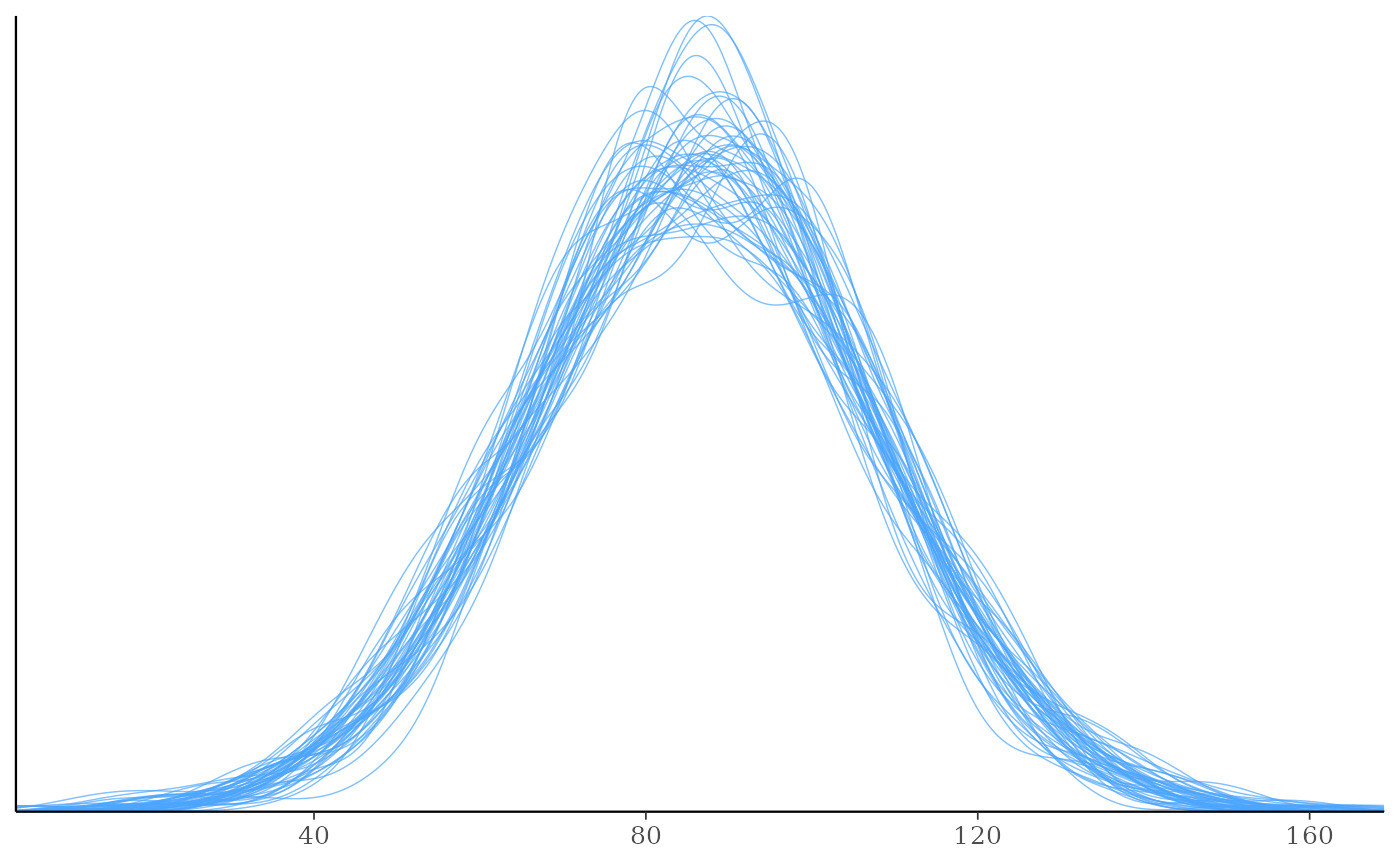
ppd_dens_overlay(ypred = preds[1:50, ])
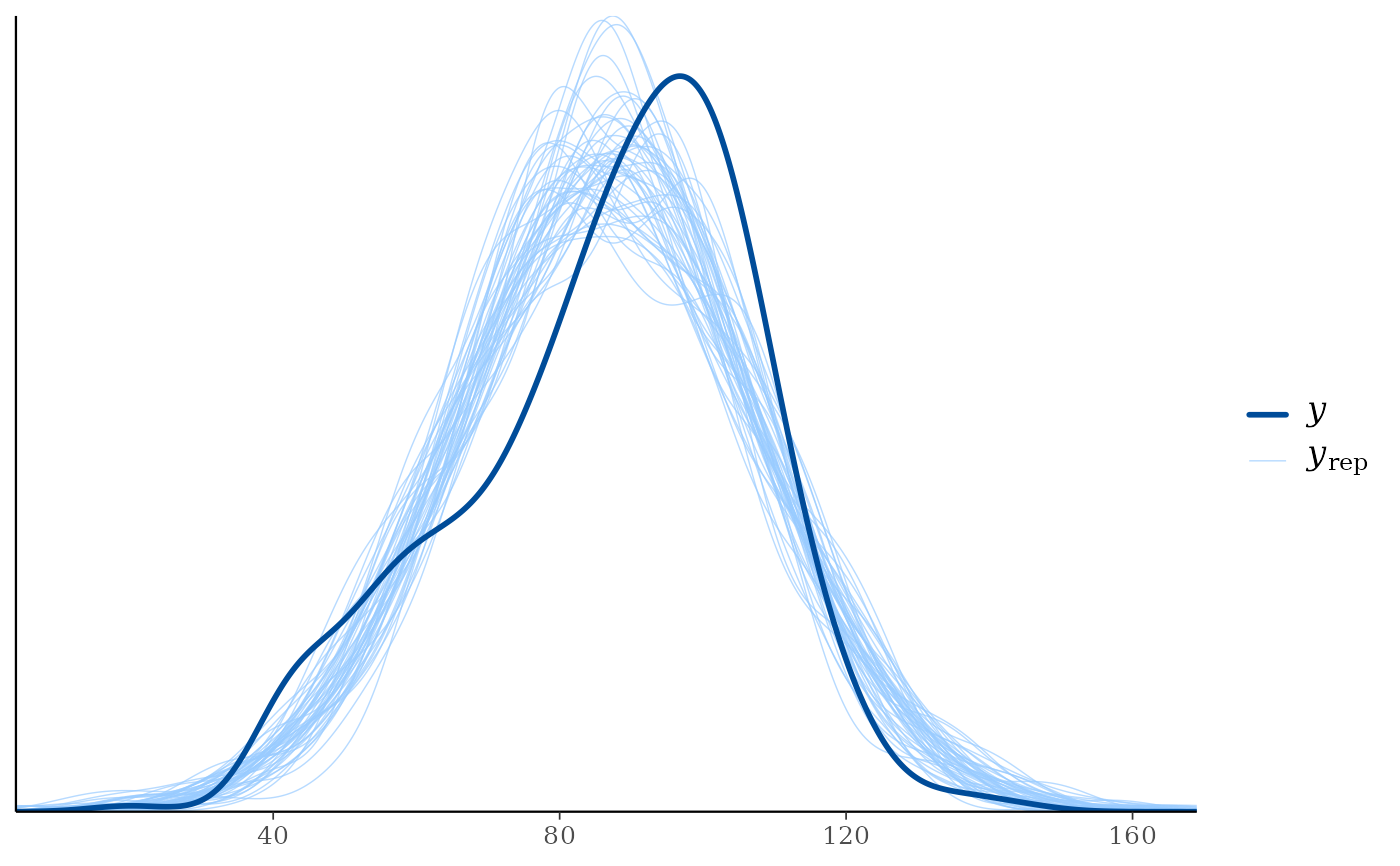
 ppc_dens_overlay(y = example_y_data(), yrep = preds[1:50, ])
ppc_dens_overlay(y = example_y_data(), yrep = preds[1:50, ])